Robotics technology, characterised by its precision, speed and reliability, is revolutionising traditional manufacturing processes, enabling businesses to meet the ever-increasing demands of modern markets. It has become evident that their integration is not merely an enhancement of the production process but a fundamental shift towards a more innovative, efficient and competitive manufacturing landscape.
This article will explore how these robotics in manufacturing contribute to operational excellence, including their role in improving product quality, reducing production costs and fostering a safer workplace.
Repetition and Efficiency
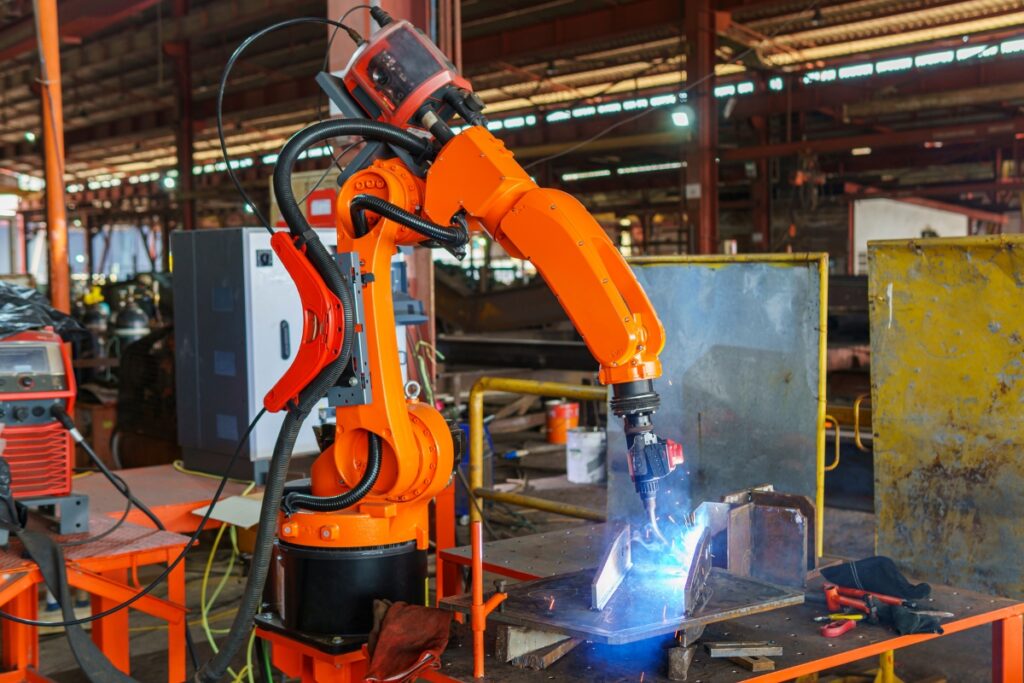
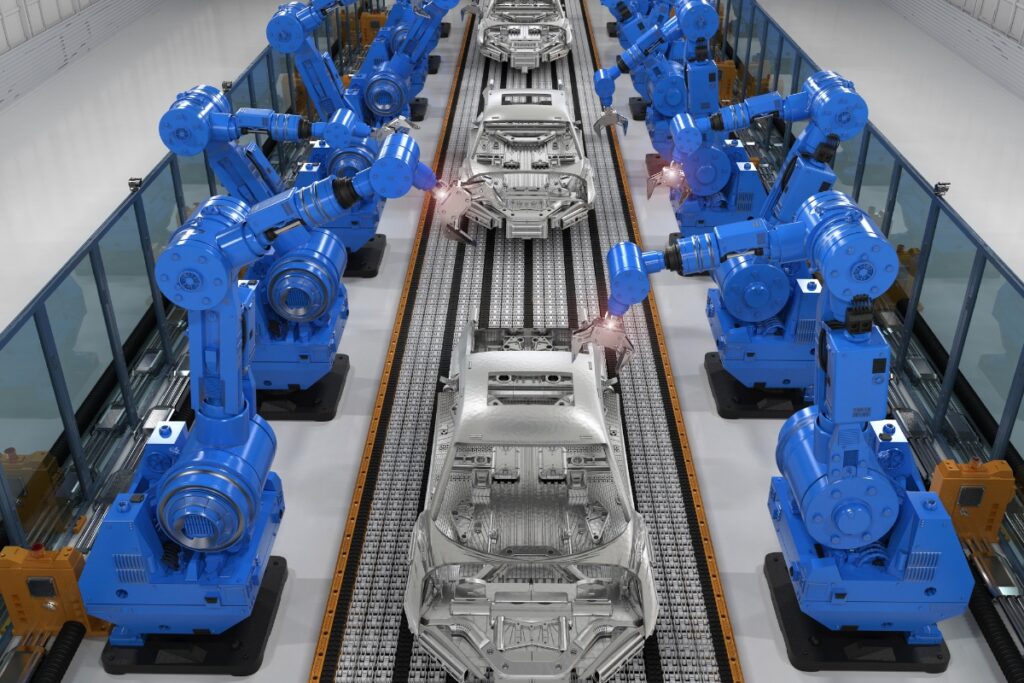
Car assembly lines, renowned for their efficiency and precision, are a prime example of how robots have revolutionised the manufacturing industry. These robots are engineered to execute repetitive tasks with speed and consistency that cannot be matched by humans who succumb to fatigue. As a result, their precision and ability to assemble and inspect reduces the likelihood of errors. Additionally, robots can be used to handle monotonous tasks like welding and painting, allowing humans the time to work on more complex and creative tasks, optimising the workforce.
Accuracy and Consistency
Robots excel in performing tasks with precision and uniformity, which are critical where the slightest error can compromise product quality. Equipped with advanced sensors and programming capabilities, robots set themselves apart from human workers by executing tasks with minute precision, ensuring production consistency. Robots can reliably maintain this high level of accuracy, which is essential in industries like electronics, automotive and aerospace, where strict specifications require the use of precision measurement equipment. Humans, despite their adaptability and creativity, struggle with monotony and precision. They are susceptible to fatigue, distraction, and concentration in environments that can compromise product quality. Robots are far more than a convenience in industries where the margin for error is minimal.
Product Quality Control
The implementation of robotics in manufacturing significantly enhances product quality control. Robots, with their ability to perform tasks accurately and consistently, minimise human error, a common source of defects in manufacturing. Advanced robotics equipped with vision systems and sensors can also inspect and detect quality issues in real time during production, ensuring that only products meeting the highest standards reach the market. This proactive approach to quality control safeguards brand reputation and reduces the costs associated with recalls and repairs. It should be noted that although robotics can play a part in quality control, human checks are also necessary in some instances.
Waste and Sustainability
Robotics aids in advancing manufacturing sustainability by optimising material usage and reducing waste, ultimately lowering environmental pollution and promoting safer waste management practices. Robots can also handle hazardous materials, safeguarding humans from long-term health issues.
Moreover, robots can be programmed to optimise energy usage, contributing to lower carbon footprints. Reducing waste and improving efficiency can also increase cost savings, making sustainable practices both environmentally friendly and economically beneficial.
Flexibility and customisation
Modern robotics in manufacturing can be quickly reprogrammed to adapt to new tasks, allowing manufacturers to respond rapidly to market changes and consumer demands. This innovative ability is particularly beneficial in industries with standard product customisation and short product life cycles. Robots can easily switch between tasks, enabling mass customisation and small batch production without sacrificing efficiency.
For prototyping products, this means faster replication, reducing costs while enhancing innovation, and robotic systems can easily handle complex tasks and adjustments. This allows for more creative product designs, giving inventors a competitive edge in the market.
Competitive and Relevant
Staying relevant in the market requires embracing technological advancements, and robotics offers a pathway to modernise production, explore new business models and capture new market opportunities. This strategic adoption of robotics is essential for businesses aiming to maintain a competitive edge, allowing them to cater to niche markets and respond to the growing demand for sustainable products. It’s about keeping pace with technological trends and seizing the opportunity to lead in a technology-driven marketplace.
Health and Safety
By taking on dangerous tasks, such as handling toxic materials or operating in hazardous conditions, robots reduce the risk of accidents, long-term injuries or sickness among human workers. This protects employees and reduces the potential financial liabilities associated with workplace accidents. Robots can also perform tasks with high precision, reducing the occurrence of repetitive strain injuries common in manual operations. Robotics adopts a safer and healthier workplace, promoting worker well-being and productivity.
Continuous Improvement
Technology enables the rapid and consistent collection and processing of data. Using technologies such as Artificial Intelligence and the Internet of Things, information can be discerned that can lead to benefits such as increased safety, efficiencies and new production capabilities. Furthermore, robots themselves will have the ability to learn and adjust their operation.
Although most robotics in manufacturing has existed in the automotive industry, with advancements, it is now playing a greater role in other industries. With increased flexibility, robots are becoming multi-purpose, enabling multi-purpose production lines.