Height gauges are essential tools in precision engineering and manufacturing. Various types are available, ranging from simple manual models to advanced digital systems. Understanding their differences is crucial for selecting the right tool for your specific application.
This article will explore the main types of height gauges, highlighting their features, benefits and typical use cases to help you make informed decisions in your measurement tasks.
What is a Height Gauge?
A height gauge is a tool used to measure how tall something is or to mark a specific height on a part, such as during machining. It usually stands on a flat surface with a base, a tall vertical beam and a pointer or scriber. Height gauges are essential in jobs requiring precise measurements, like metalworking or quality assurance. They give accurate, repeatable results and can show measurements in both millimetres and inches.
Brief History: Mechanical vs Digital
Earlier devices required manual readings and relied heavily on the operator’s skill. Over time, technological advancements led to the creation of digital height gauges, which offer improved accuracy, ease of use, and data integration. Digital models can interface with computers and other devices, enabling real-time data logging and analysis. While mechanical gauges remain valued for their robustness and affordability, digital versions dominate modern precision engineering environments due to their speed, reduced human error, and versatile functionality.
Vernier, a 17th-century French scientist, mathematician, and engineer, invented the vernier scale in 1631. This invention revolutionised precision measurement and forms the basis for many modern engineering tools, including the vernier height gauge. These devices required manual readings and relied heavily on the operator’s skill. Over time, technological advancements led to the Trimos Company in 1968 creating the first digital height gauge, which offers improved accuracy, ease of use and data integration. This paved the way for rapid advancements and shaped the modern digital height gauge as we know it today.
Types of Height Gauges:
Mechanical:
Vernier Height Gauges
A vernier height gauge is a mechanical device that uses a vernier scale to measure vertical distances. It comprises a heavy base for stability, a vertical column and a sliding carriage with a vernier scale and measuring jaw or scriber. The scale allows for precise manual readings to 0.02 mm or finer.
Vernier height gauges are highly durable and built to last, making them ideal for tough industrial environments. Since they operate mechanically, they don’t require any power source, which adds to their convenience and reliability. These gauges are also cost-effective compared to digital models and are simple to maintain with minimal upkeep. However, they require skill and experience to read, which can be a barrier for less-trained users, ultimately leading to human error.
This manual height gauge is mainly used in metal fabrications and machining workshops to scribe lines or check part heights on surface plates, especially where electronic tools are impractical.
Dial Height Gauges
Dial height gauges feature a dial indicator to show readings, offering easier measurement readings than vernier scale types. They work mechanically, using rack-and-pinion movement to transmit height data to the dial face.
While dial height gauges require no batteries and are easier to read, they’re susceptible to parallax error, which can limit data recordings.
Although they’re slower than digital gauges, they’re commonly used in automotive and general manufacturing industries for quality control and part comparison where moderate precision is needed without digital complexity.
Digital:
Laser Height Gauges
Laser height gauges are non-contact measurements that use laser beams to determine height. They’re ideal for delicate or irregular surfaces, and many models include a digital display for easy reading.
Unlike manual devices, they’re fast and require power. They’re also highly accurate, making data output easier. While they’re suitable for non-contact applications, they’re highly sensitive to dust and vibrations.
Laser height gauges are used in the semiconductor and electronics industries to measure circuit board or wafer thicknesses, where contact with the product could damage it.
Ultrasonic Height Gauges
Ultrasonic height gauges emit ultrasonic waves and measure the time it takes for the echo to return. The time delay is translated into height measurements.
This digital gauge type is non-contact and suitable for measuring soft or moving objects. Unlike laser height gauges, ultrasonic can still work effectively in dusty environments. However, their accuracy can be affected by temperature and may require calibration.
This digital tool is ideal for factories in the food industry or rubber manufacturing, where contact measurement could deform the materials or be unsafe due to contamination concerns.
Digital Vernier Height Gauges
This digital evolution of the traditional vernier height gauge combines mechanical construction with electronic readouts. Measurements are displayed digitally, improving speed and reducing error.
Measurements displayed digitally are easier to read and increase accuracy and precision.
They even include data ports for recording. However, as they require batteries or power to perform, they’re more expensive than their mechanical version.
Digital vernier height gauges are mainly used in high-precision mechanical workshops and aerospace industries for efficient, accurate, and repeatable part inspections and component profiling.
Digital Dial Height Gauges
Digital dial height gauges resemble the structure of manual dial gauges, though they use electronic sensors instead of traditional mechanical dials.
Though they’re complex to use initially, their digital interface provides clear and precise readings, making them easier to interpret.
Digital dial heights are widely used in medical device manufacturing, where small tolerances and consistent results are essential during component verification and assembly alignment.
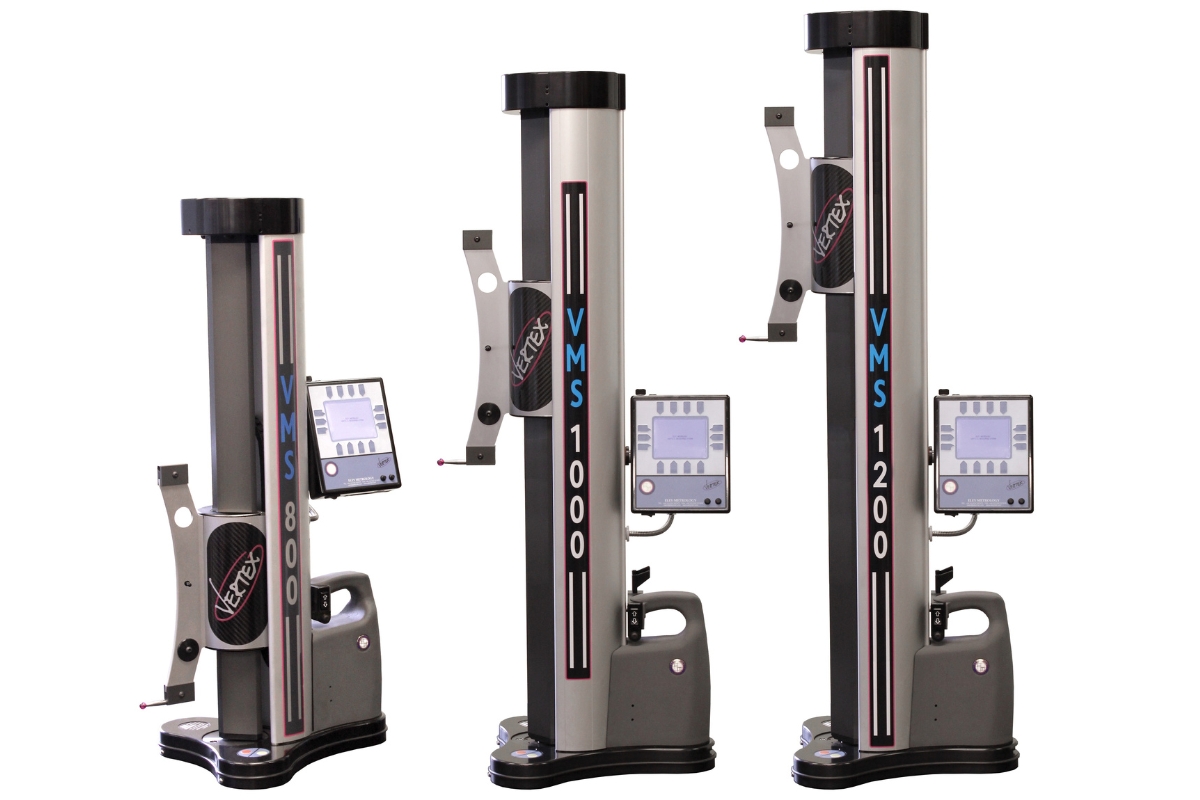
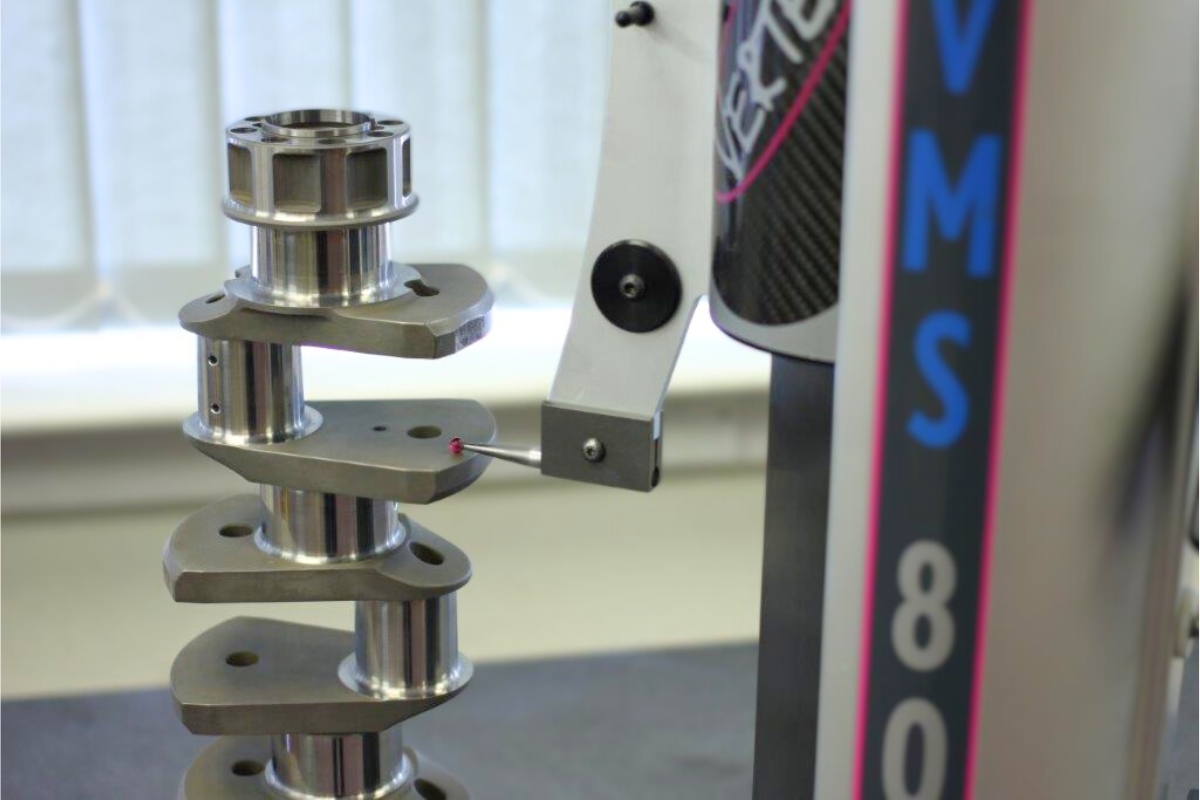
The Vertex VMS
The Vertex VMS (Vertical Measurement System) incorporates advanced digital height gauge features such as touchscreens, programmable measurement routines, and 3D scanning capabilities.
This advanced digital height gauge features an intuitive interface, delivers exceptional precision, offers extensive data logging capabilities and is compatible with automated systems.
It is ideal for complex, high-accuracy measurements in industries where precision is critical, such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing. These industries require ultra-precise component inspection and documentation, especially for complex shapes and tight tolerances.

Jeff Eley is the founder and managing director of Eley Metrology, a leading company in the precision measurement industry. With decades of experience in metrology, Jeff has established himself as a respected figure in the field. Under his leadership, Eley Metrology has become renowned for its expertise in coordinate measuring machines (CMMs), digital height gauges, and granite metrology products. Jeff’s vision has driven the company to develop innovative solutions, including custom-designed CMMs and the flagship long-bore measurement machine (LBM). His commitment to excellence and customer-centric approach has positioned Eley Metrology as a trusted provider of high-precision measurement tools and services for industries such as aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing.